On-Page SEO is the critical art of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and attract more organic traffic. Unlike other SEO strategies that focus on external factors, on-page SEO concentrates on the elements directly within your web page that you can control and enhance.
At its core, on-page SEO involves carefully crafting and structuring your webpage’s content, HTML source code, and visual elements to make them as search-engine friendly as possible. This approach helps search engines understand your content’s relevance, quality, and value to potential readers. The first component of On-Page Seo is:
High Quality Content:
satisfies search intent, presents content effectively, provides accurate and up to date information, demonstrates expertise & trustworthiness etc.
This can be done by:
Covering Topics Thoroughly
- Keyword Research: Identify all relevant keywords, subtopics, and questions users commonly ask about your main topic.
- Organize Content Structure: Use a logical structure that covers each subtopic or question.
- Include Supporting Details: Cover definitions, history, advantages and disadvantages, step-by-step guides, and any relevant aspects.
- Optimize for Search Intent*

Providing Helpful Examples
- Use Case Studies: If you have data or experiences from your business.
- Create Scenarios: Hypothetical scenarios can illustrate abstract ideas.
- Illustrate with Numbers: Include relevant data and statistics in examples.
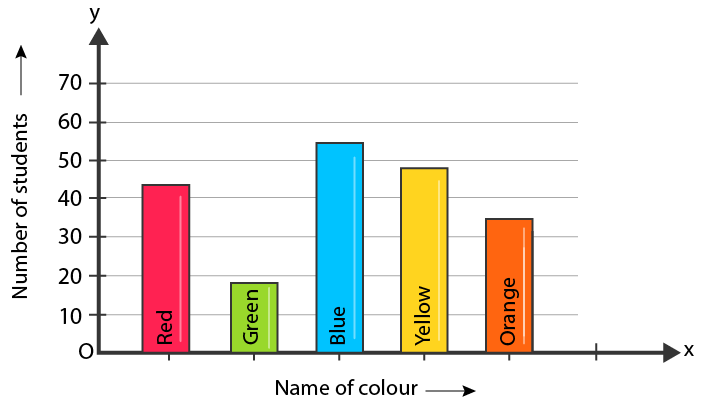
Adding Original Data
- Conduct Surveys: Run a survey within your industry to gather data on trends.
- Use Internal Data: Analyze data from your own business or website, such as customer preferences, purchase patterns, or website metrics, to derive new findings.
- Create Visual Data: Present your data in an easy-to-understand format using graphs, charts, and infographics, as these are more likely to be shared and linked to.

Creating Original Media
- Design Custom Images: Create infographics, illustrations, or icons that visually explain key points or data in your content.
- Embed Videos: Videos, such as how-to guides, product demos, or tutorials, can break down complex topics and make them more engaging.
- Develop Interactive Media: Interactive tools like calculators, quizzes, or maps can make content engaging.

Using Reliable Sources in Hyperlinks
- Link to Authoritative Sites: Reference studies, articles, and data from trusted sources like government websites.
- Link to Related Articles: Provide links to articles that give context to your content or further explain complex ideas.
- Cite Recent Data: Whenever possible, use the most recent data available. Outdated information can hurt credibility.
- Avoid Over-Linking: Include external links only when they add genuine value.
Headers/Titles/Paragraphs
All must follow a strict hierarchy with titles being the most important and paragraphs the least.
Typically, you should only have one title per web page, this allows for web crawlers to easily understand generally what your webpage is about, headers can help the crawler to understand subcategories and paragraphs can help the crawler understand detailed information pertaining to the page.
Keywords Should Be Implemented In
- First paragraph
- Title
- H1, H2 & H3 Tags
- Subheadings like H2 & H3 should contain secondary keywords, for example dog food would be a primary keyword and the brand name would be secondary)
- Meta Descriptions(Page summary in search results)
- Website Slug(This is the specific page you are on ie Shop/Cookies/Chocolate-Chip, Chocolate-Chip is a Website Slug)
It is important to use correct grammar and syntax when trying to implement keywords into your content as search engines have contextual understanding as well as Natural Language Processing (NLP) which is a process that interprets the meaning of words and phrases.

Keyword Research
Keyword research is the process of identifying and analyzing the search terms that people enter into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. It’s a foundational step in SEO and content creation, as it helps you understand what topics resonate with your target audience and the language they use to search for them.
When conducting keyword research, it is important to:
Define Your Goals:
What is your niche? Who are you trying to appeal to?
It is important to understand first what search intent you are trying to achieve, there are multiple types of search intent:

- Navigational search intent (Looking for a specific page on a site) would apply to all websites, this would have to do with things like keyword mapping ie webarc.io/shop/options. The mapping of the subcategories shop & options are the subcategories that are being mapped for.
- Keyword Mapping: With this in mind it’s important to design the page that is being mapped for with the url name that has been given for that page. For example if you map “shop” into the url you want to make sure the headers/titles/content on that page are related to “shop” as well.
- Informational search intent(Finding general information) has to do with things like blogs and articles. When someone searches for an answer to a question they would be categorized as having “Informational” search intent.
- Key Differences: Similarly to navigational search intent you want to design the pages keywords around the topic you are trying to discuss, the only difference is that this type of intent is more general where navigational is more specific.
- Commercial search intent is when customers are making searches that are aimed at comparing items. This can be optimized for by making it clear on your listing how your product is valuable and how it competes on price.
- Transactional search intent: this type of intent is aimed at customers that are looking to make a specific purchase, this can be optimized similarly to Commercial intent except with an enthesis on keywords that correlate with making a direct purchase.
Once you have determined what search intent you are aiming for you can then start to research what keywords you want to use in your articles. Typically, you would want to start by analyzing your competitors with software like SEMRUSH in order to find keywords relating to your competitor and for your search intent.
SEMRUSH is a powerful digital marketing tool primarily used for search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, content marketing, and competitive analysis. It offers a suite of tools that helps marketers, content creators, and businesses improve their online visibility and track various aspects of their digital performance.
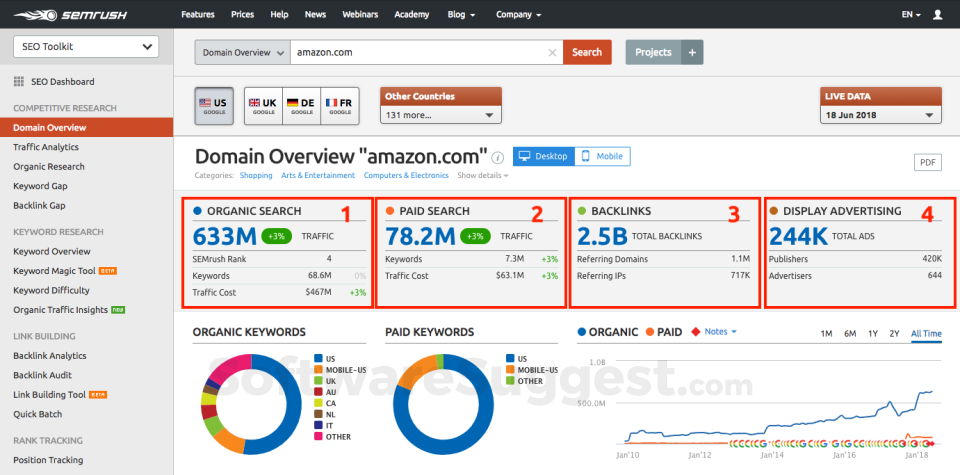
SEMRUSH can be used to identify keywords that have high rankability which basically means keywords that are aligned with your competitors but aren’t being utilized by anyone.
SEMRUSH offers two primary keyword research tools: Keyword Gap & Keyword Magic. Both of these tools analyze search internet as well as Personal keyword Difficulty (PKD%).
PKD% takes into account multiple factors like:
- Current Rankings: This is how high your site ranks for this keyword currently.
- Domain Authority: This is how credible your overall cite has been determined.
- Topical Authority: This is how credible your website has been deemed on a specific topic.
Keyword Gap Allows you to analyze the difference in keywords of your competitors. Analyzing this data can be done using PKD%, search intent as well filters that show untapped keywords.

Keyword magic can be used to find relevant keywords that pertain to a seed keyword. There are 4 types of keywords:
- Broad: Any variation of seed term/s in any order.
- Phrase: Contains your seed word/s in any order.
- Exact: Contains seed term/s in order.
- Related: Similar engine results.
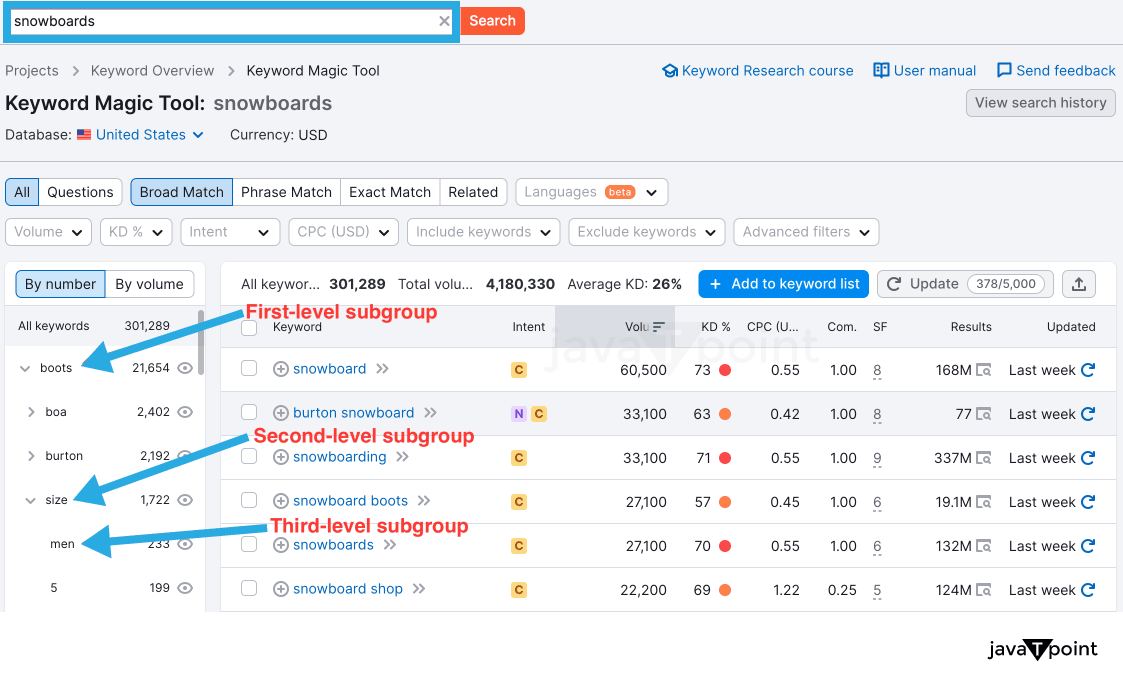
Once you have identified some keywords, try and implement them into your content, this brings us to our next topic…
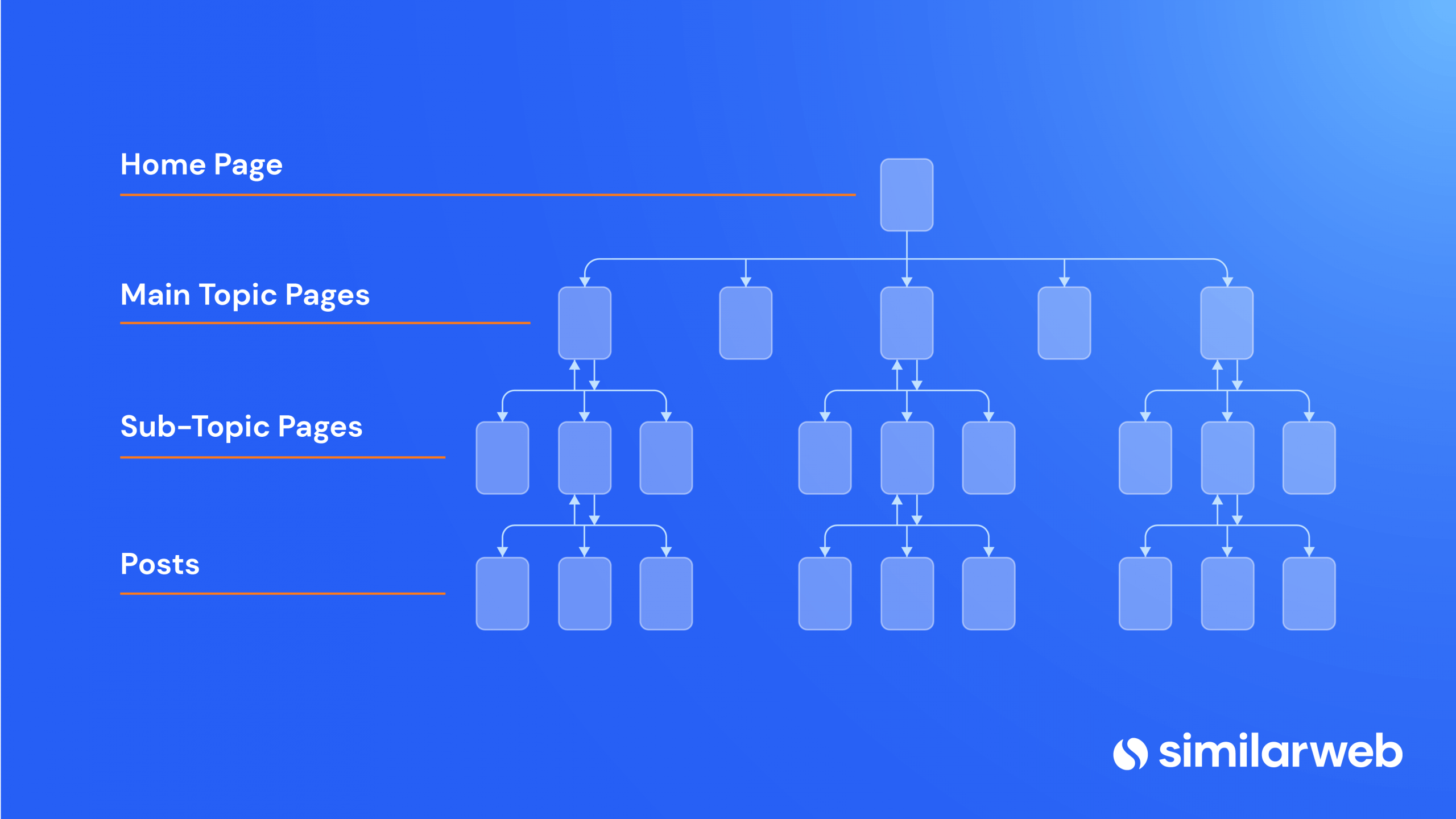
What are HTML sitemaps?
HTML sitemaps are web pages that list all or most of the key pages on a website in an organized, hierarchical structure, helping users and search engines easily find and navigate to specific content. HTML sitemaps improve user experience by providing a clear map of the site layout, and they’re useful for SEO as they allow search engine crawlers to more easily understand the structure of the website and index pages more efficiently.

Benefits of an HTML Sitemap
Improved Navigation: For users, especially on larger sites, an HTML sitemap can make it easier to locate a particular page or section.
Enhanced SEO: HTML sitemaps provide additional paths for search engines to find and index pages.
Organization: It offers a bird’s-eye view of the website structure, which can be especially useful for content-heavy sites.
Steps to Implement an HTML Sitemap
- Plan Your Sitemap Structure:
- Determine which pages should be included. Typically, you’ll want to include main category pages, subcategories, and any important individual pages (such as blog posts or product pages).
- Organize pages in a hierarchy that makes sense for your site’s structure.
- Create an HTML Sitemap Page:
- Create a new HTML page (e.g., sitemap.html) and add it to your website.
- Use a clean, organized layout, such as nested lists, to represent your pages and sections.
- Each item in the list should contain a link to a page on your website, allowing both users and crawlers to access it.
3. Link to the Sitemap:
- Place a link to your HTML sitemap in the footer or main navigation of your website so it’s accessible from any page.
4. Test and Optimize:
- Make sure all links work and that the page is easily navigable.
- Regularly update the HTML sitemap as new pages are added or removed from the site to keep it accurate.
Maintaining the HTML Sitemap
Once set up, an HTML sitemap should be updated whenever there’s a significant change to your site structure. For dynamic websites, you might consider using scripts to auto-generate and update the sitemap. If you wanted to go more in depth to make sure that your sitemap is made well SEMrush offers a few different Insights on various aspects:
- Coverage:
- Compare the total number of pages linked in the HTML sitemap with the total number of pages on the site.
- Check if any critical pages are missing or duplicated.
- Link Depth:
- Navigate to the Internal Linking section.
- Assess the click depth of pages linked from the sitemap. Pages should ideally be accessible within 2–3 clicks from the homepage.
- Crawlability:
- Verify that the links in the sitemap are marked as crawlable by SEMrush.
- Use the Indexability tab to confirm that all linked pages can be indexed by search engines.
- Broken or Redirected Links:
- SEMrush highlights any links in the sitemap that return a 404 error, 301/302 redirect, or other status codes.
- Review and fix these links in your sitemap.
- Content Quality:
- Use the Page Issues report to ensure that linked pages have optimized titles, meta descriptions, and no duplicate content.
What’s a Meta Description?
A Meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary of a webpage’s content. It’s typically displayed in search engine results pages (SERPs) under the page title, helping users understand the relevance of the page to their search. While it doesn’t directly impact search rankings, a well-written meta description can improve click-through rates, as it gives searchers a compelling reason to click on your link.

Key Features of a Good Meta Description
- Length: Aim for about 150–160 characters, as this fits well within the display limits on most SERPs.
- Relevance: Ensure the description accurately reflects the content on the page.
- Keywords: Include primary keywords naturally to signal relevance to search engines.
- Compelling Text: Write in a way that engages users and encourages them to click, such as by highlighting unique benefits or solving a problem the searcher might have.
Steps to Craft and Add a Meta Description
- Write the Meta Description:
- Keep it concise, informative, and compelling.
- Include the main keyword naturally.
- Mention unique aspects of the content, like a special feature or offer.
- Add the Description to the HTML:
- Place it in the <head> section, as shown above. This allows search engines to detect it right away.
- Check and Adjust:
- If your page is indexed in Google, review how your meta description displays in search results.
- You can use tools like Google Search Console to see if your description impacts click-through rates and adjust it if needed.
Conclusion
Implementing on-page SEO strategies is essential for any business looking to enhance its online presence, drive organic traffic, and boost conversions. By creating high-quality content that satisfies search intent, structuring pages for clarity and hierarchy, utilizing effective keyword research, and optimizing technical elements like meta descriptions and HTML sitemaps, businesses can improve their visibility on search engines and establish credibility in their industry.
These efforts not only attract the right audience but also provide a better user experience, fostering trust and engagement. When executed consistently, on-page SEO can become a powerful tool for sustainable growth and long-term success in the digital landscape.
